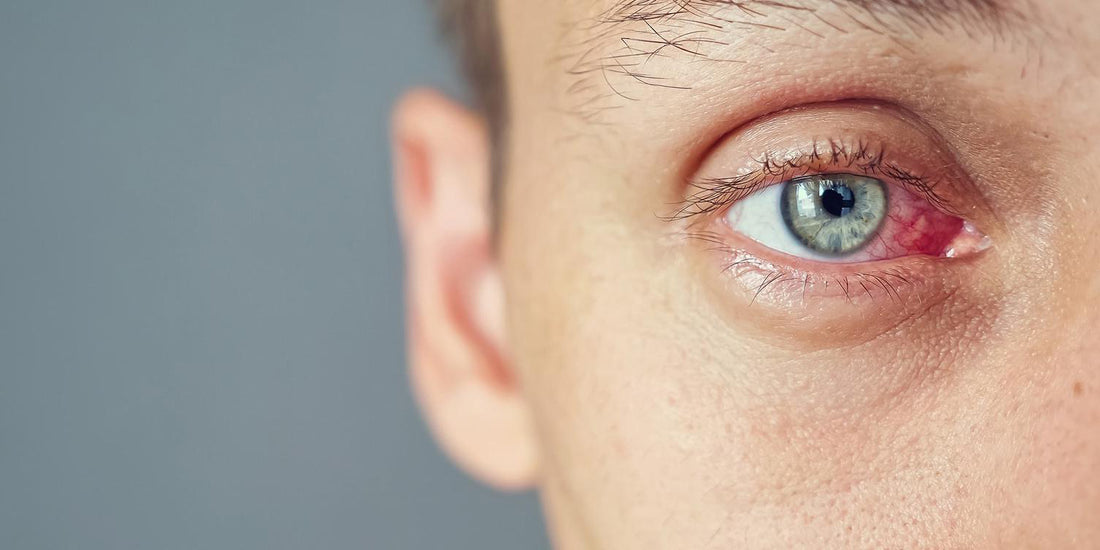
Understanding Eye Infections: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options for Conjunctivitis, Keratitis, Uveitis, Endophthalmitis, and Blepharitis
Share
Welcome to Look Optometry, where our commitment to eye health extends beyond routine exams to understanding and addressing complex issues like eye infections. I'm Dr. Shailinder Bhullar, and I'm passionate about providing comprehensive care that goes beyond the surface, diving into the intricacies of conditions like conjunctivitis, keratitis, uveitis, endophthalmitis, and blepharitis.
Eye infections can range from common conditions like conjunctivitis (pink eye) to more serious issues like keratitis and endophthalmitis. Each infection presents its own set of causes, symptoms, and treatment options, requiring a nuanced approach to diagnosis and care.

Conjunctivitis, often known as pink eye, can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or allergies. Symptoms may include redness, itching, and discharge. Treatment options vary depending on the cause, ranging from antiviral medications to antibiotics or simple home remedies.
Keratitis, on the other hand, involves inflammation of the cornea and can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. Symptoms often include eye pain, blurred vision, and sensitivity to light. Treatment may involve antibiotics, antifungal medications, or corticosteroids, depending on the underlying cause.
Uveitis, a condition characterized by inflammation of the uvea, can have various causes, including autoimmune disorders, infections, or trauma. Symptoms typically include eye pain, redness, and blurred vision. Treatment options may include corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, or anti-inflammatory drugs to manage the inflammation effectively.
Endophthalmitis is a severe infection that can occur after eye surgery, trauma, or as a result of an underlying infection spreading to the eye. Symptoms may include severe eye pain, vision loss, and redness. Treatment often involves intravitreal antibiotics, vitrectomy, and systemic antibiotics to control the infection and prevent complications.
Finally, blepharitis involves inflammation of the eyelids and can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungal infections. Symptoms may include red, swollen eyelids, itching, and flaking skin. Treatment typically involves warm compresses, eyelid hygiene practices, and sometimes antibiotics to manage the condition effectively.
At Look Optometry, we're committed to raising awareness about eye infections and providing tailored care for each individual's needs. Whether you're dealing with conjunctivitis, keratitis, uveitis, endophthalmitis, or blepharitis, we're here to help you understand your condition and explore the best treatment options available.
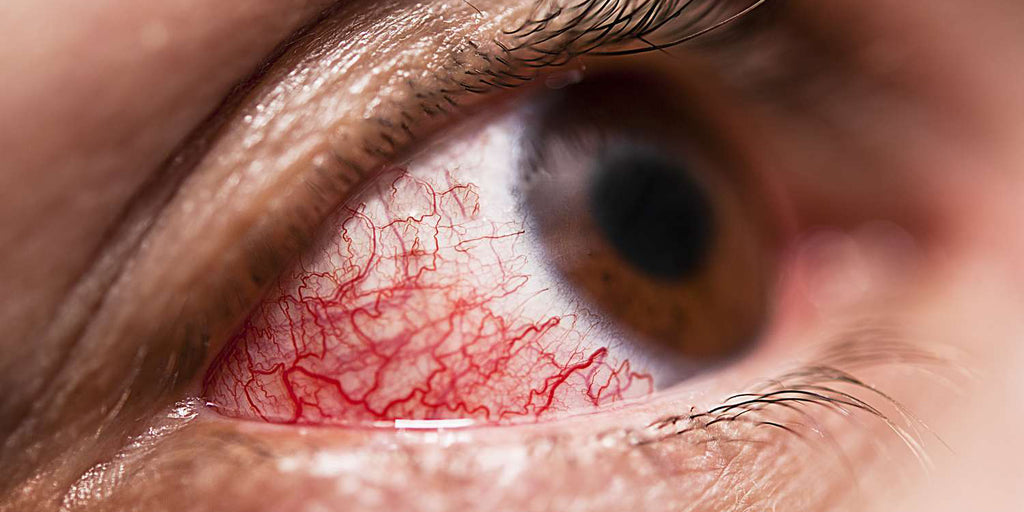
What is Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye)
Conjunctivitis, commonly known as pink eye, is a prevalent eye infection that can affect people of all ages. At Look Optometry, we understand the importance of recognizing the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition to ensure optimal eye health for our patients.
Causes of Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye):
Conjunctivitis can be caused by various factors, including viruses, bacteria, and allergens. Viral conjunctivitis is often associated with upper respiratory infections, such as the common cold, and tends to be highly contagious. Bacterial conjunctivitis can result from bacterial infections, leading to redness, discharge, and discomfort. Allergic conjunctivitis, on the other hand, is triggered by allergens such as pollen, pet dander, or dust mites, causing itching, tearing, and redness.
Symptoms of Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye):
The symptoms of conjunctivitis can vary depending on the underlying cause but commonly include redness in the whites of the eyes, itching or burning sensation, excessive tearing, and discharge, which may be clear or yellowish in color. Patients may also experience sensitivity to light and blurred vision, particularly in cases of severe inflammation.
Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye) Treatment Options:
Treatment for conjunctivitis depends on the cause and severity of the infection. Viral conjunctivitis often resolves on its own within a few days without specific treatment, although symptomatic relief may be provided through the use of lubricating eye drops and cold compresses. Bacterial conjunctivitis typically requires antibiotic eye drops or ointment to clear the infection and alleviate symptoms. Allergic conjunctivitis may be managed with antihistamine eye drops, avoidance of allergens, and cold compresses to reduce inflammation.
How to prevent Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye):
Preventing the spread of conjunctivitis is essential, especially in cases of viral or bacterial infection. Practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing, avoiding touching the eyes, and refraining from sharing personal items like towels or eye makeup, can help reduce the risk of transmission. Additionally, individuals with allergic conjunctivitis should take steps to minimize exposure to allergens and consider using protective eyewear when necessary.
What is Keratitis?:
Keratitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the cornea, the transparent layer covering the front of the eye. It can be caused by various factors, including bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infections, as well as injuries or underlying health conditions. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for keratitis is essential for effective management and preservation of eye health.
Causes of Keratitis:
Keratitis can develop as a result of different factors, with infectious and non-infectious causes being the most common. Infectious keratitis often occurs due to bacterial or viral infections, which can enter the eye through trauma, contact lens wear, or pre-existing eye conditions. Fungal keratitis is less common but can occur in individuals with a history of trauma, exposure to contaminated water or soil, or compromised immune systems. Non-infectious keratitis may be caused by environmental factors such as ultraviolet (UV) radiation, dry eye syndrome, or chemical exposure.
Symptoms of Keratitis:
The symptoms of keratitis can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common symptoms may include eye pain or discomfort, redness, blurred or decreased vision, sensitivity to light (photophobia), excessive tearing, and the sensation of a foreign body in the eye. In cases of infectious keratitis, patients may also experience discharge, inflammation, and corneal ulceration, which can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
Keratitis Treatment Options:
Treatment for keratitis aims to address the underlying cause of the inflammation and alleviate symptoms to prevent complications and promote healing. In cases of infectious keratitis, prompt administration of antimicrobial therapy, such as topical or oral antibiotics, antiviral medications, or antifungal agents, is crucial to control the infection and prevent further corneal damage. Additionally, supportive measures such as lubricating eye drops, pain relievers, and protective eyewear may be recommended to enhance comfort and aid in the healing process. In severe cases of keratitis with corneal ulceration or vision-threatening complications, surgical intervention, such as corneal transplantation or amniotic membrane grafting, may be necessary to preserve vision and restore corneal integrity.
How to prevent Keratitis:
Preventing keratitis involves adopting measures to reduce the risk of infection and protect the eyes from potential hazards. Proper contact lens hygiene, including regular cleaning, disinfection, and replacement of lenses, is essential to minimize the risk of microbial contamination and keratitis associated with contact lens wear. Avoiding eye trauma, practicing good ocular hygiene, and wearing protective eyewear when engaging in activities that pose a risk of injury or exposure to environmental irritants can also help prevent keratitis and maintain optimal eye health.
What is Uveitis?:
Uveitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the uvea, the middle layer of the eye that includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. It can be caused by various factors, including autoimmune disorders, infections, trauma, or underlying systemic diseases. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for uveitis is crucial for effective management and preservation of eye health.
Causes of Uveitis:
Uveitis can develop as a result of different factors, with autoimmune disorders and infections being among the most common causes. Autoimmune uveitis occurs when the body's immune system mistakenly targets the tissues of the eye, leading to inflammation and tissue damage. Infections, such as viral, bacterial, fungal, or parasitic, can also trigger uveitis by directly invading the eye or as a secondary complication of systemic infections. Other potential causes of uveitis include trauma, inflammatory conditions such as sarcoidosis or Behcet's disease, and certain medications or toxins.
Symptoms of Uveitis:
The symptoms of uveitis can vary depending on the specific area of the uvea affected and the underlying cause of the inflammation. Common symptoms may include eye pain, redness, blurred vision, sensitivity to light (photophobia), floaters (spots or cobwebs in the field of vision), and decreased visual acuity. In some cases, uveitis may be associated with systemic symptoms such as fever, joint pain, skin rash, or fatigue, particularly in cases of autoimmune or infectious uveitis.
Uveitis Treatment Options:
Treatment for uveitis aims to control inflammation, alleviate symptoms, and prevent complications to preserve vision and ocular health. The choice of treatment depends on the underlying cause, severity, and location of uveitis, as well as the patient's overall health status. Corticosteroids, in the form of eye drops, injections, or oral medications, are often used as first-line therapy to reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms. Immunosuppressive agents, such as methotrexate, azathioprine, or cyclosporine, may be prescribed to suppress the immune response and prevent recurrent inflammation in cases of autoimmune uveitis. In severe or refractory cases of uveitis, biologic agents or surgical intervention, such as vitrectomy or implantation of intraocular devices, may be necessary to control inflammation and preserve vision.
How to prevent Uveitis:
Preventing uveitis involves addressing modifiable risk factors and managing underlying systemic conditions to reduce the risk of inflammation and ocular complications. Patients with autoimmune disorders should work closely with their healthcare providers to manage their condition effectively and minimize the risk of uveitis flare-ups. Practicing good ocular hygiene, avoiding eye trauma, and seeking prompt medical attention for any signs or symptoms of uveitis can also help prevent complications and maintain optimal eye health.
What is Endophthalmitis?:
Endophthalmitis is a severe and potentially sight-threatening condition characterized by inflammation of the internal structures of the eye, including the vitreous humor and the anterior or posterior chambers. It can develop as a result of various factors, such as post-surgery complications, trauma, or as a secondary infection spreading from other parts of the body. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for endophthalmitis is essential for timely intervention and preservation of vision.
Causes of Endophthalmitis:
Endophthalmitis can occur following intraocular surgery, such as cataract extraction or vitrectomy, as a complication of ocular trauma, or as a result of an infection spreading from other parts of the body. Post-operative endophthalmitis is often caused by bacterial contamination during surgery, leading to infection and inflammation within the eye. Traumatic endophthalmitis may result from penetrating injuries or foreign body penetration, introducing microorganisms into the eye and triggering an inflammatory response. Endogenous endophthalmitis, on the other hand, occurs when infectious agents travel through the bloodstream and reach the eye, typically in patients with systemic infections or immunocompromised conditions.
Symptoms of Endophthalmitis:
The symptoms of endophthalmitis can develop rapidly and may include severe eye pain, redness, blurred vision, floaters (spots or cobwebs in the field of vision), photophobia (sensitivity to light), and eyelid swelling. Patients may also experience decreased visual acuity, intraocular pressure changes, and hypopyon (pus accumulation) in the anterior chamber. In severe cases, endophthalmitis can lead to vision loss, retinal detachment, or even loss of the eye if not promptly diagnosed and treated.
Endophthalmitis Treatment Options:
Treatment for endophthalmitis requires prompt and aggressive intervention to control infection, reduce inflammation, and preserve vision. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the infection, the causative microorganism, and the patient's overall health status. Empirical antibiotic therapy, typically consisting of broad-spectrum intravitreal antibiotics, is initiated immediately to cover a wide range of potential pathogens while awaiting culture results. Corticosteroids may also be administered to reduce inflammation and prevent tissue damage. In some cases, vitrectomy surgery may be necessary to remove infected vitreous fluid, debris, and inflammatory cells, allowing for better visualization and treatment of the underlying infection.
How to prevent Endophthalmitis:
Preventing endophthalmitis involves implementing strict aseptic techniques during intraocular surgery to minimize the risk of bacterial contamination. Surgeons and operating room personnel should adhere to rigorous sterile protocols, including proper hand hygiene, disinfection of surgical instruments and equipment, and use of sterile drapes and gloves. Patients undergoing intraocular procedures should be educated about the signs and symptoms of post-operative infection and instructed to seek immediate medical attention if any concerns arise.
What is Blepharitis?:
Blepharitis is a common and chronic condition characterized by inflammation of the eyelids, specifically the eyelid margins where the eyelashes are located. It can be caused by various factors, including bacterial, viral, or fungal infections, as well as underlying skin conditions or poor eyelid hygiene. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for blepharitis is essential for effective management and relief of symptoms.
Causes of Blepharitis:
Blepharitis can develop as a result of different factors, with bacterial overgrowth and skin conditions being among the most common causes. Bacterial blepharitis occurs when bacteria, typically Staphylococcus species, proliferate along the eyelid margins, leading to inflammation and irritation. Viral or fungal infections, such as herpes simplex virus or seborrheic dermatitis, can also contribute to blepharitis by causing inflammation and scaling of the eyelid skin. Other potential causes of blepharitis include meibomian gland dysfunction, rosacea, allergies, or demodex mite infestation.
Symptoms of Blepharitis:
The symptoms of blepharitis can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the inflammation. Common symptoms may include redness and swelling of the eyelids, itching or burning sensation, irritation or grittiness, excessive tearing, and crusting or flaking of the eyelid margins. Patients may also experience sensitivity to light (photophobia), blurred vision, or the sensation of a foreign body in the eye. In some cases, blepharitis may lead to complications such as eyelid thickening, loss of eyelashes, or secondary infections.
Blepharitis Treatment Options:
Treatment for blepharitis aims to reduce inflammation, improve eyelid hygiene, and alleviate symptoms to prevent recurrence and complications. The choice of treatment depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Warm compresses and gentle eyelid scrubs with baby shampoo or commercial lid hygiene products are often recommended to help loosen debris and crusts, reduce bacterial load, and promote healthy eyelid function. Antibiotic ointments or drops may be prescribed to control bacterial overgrowth and prevent secondary infections. In cases of meibomian gland dysfunction, treatments such as meibomian gland expression, eyelid massage, or lipid-based artificial tears may be beneficial to improve tear film quality and relieve symptoms.
How to prevent Blepharitis:
Preventing blepharitis involves adopting good eyelid hygiene practices and addressing predisposing factors to minimize the risk of inflammation and recurrence. Patients should be educated about the importance of regular eyelid hygiene, including daily eyelid cleansing and warm compresses, to maintain clean and healthy eyelids. Avoiding eye rubbing, minimizing exposure to potential irritants or allergens, and managing underlying skin conditions or systemic diseases can also help prevent blepharitis and promote overall ocular health.
Prevention Tips for Eye Infections
Preventing eye infections is essential for maintaining optimal eye health and vision. While some eye infections are unavoidable, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of contracting and spreading infections. At Look Optometry, we prioritize preventive care and offer the following tips to help you protect your eyes from infection:
Practice Good Hand Hygiene:
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially before touching your eyes or handling contact lenses.
- Use hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol if soap and water are not readily available.
Avoid Touching Your Eyes:
- Refrain from rubbing or touching your eyes with unwashed hands, as this can introduce bacteria, viruses, or other pathogens into the eyes.
Proper Contact Lens Care:
- Follow proper hygiene practices when handling contact lenses, including cleaning, disinfecting, and storing them as directed by your eye care professional.
- Avoid sleeping in contact lenses unless prescribed by your eye doctor, as overnight wear can increase the risk of eye infections.
Avoid Sharing Personal Items:
- Do not share towels, pillows, eye makeup, or other personal items that come into contact with the eyes to minimize the risk of spreading infections.
Protect Your Eyes:
- Wear protective eyewear, such as safety glasses or goggles, when engaging in activities that pose a risk of eye injury or exposure to harmful substances.
- Use sunglasses with UV protection to shield your eyes from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which can increase the risk of certain eye conditions.
Seek Prompt Medical Attention:
- If you experience symptoms of an eye infection, such as redness, pain, discharge, or changes in vision, seek prompt medical attention from an eye care professional.
- Avoid self-diagnosis and over-the-counter remedies, as they may not effectively treat the underlying cause of the infection and could potentially worsen the condition.
Follow Post-Surgery Instructions:
- If you undergo eye surgery, follow your surgeon's post-operative instructions carefully to minimize the risk of complications, including infection.
- Attend follow-up appointments as scheduled to monitor your recovery and ensure optimal healing.
By following these preventive measures, you can reduce your risk of contracting eye infections and promote long-term eye health and vision. At Look Optometry, we're committed to supporting you in maintaining healthy eyes and providing personalized care to address your individual needs. If you have any questions or concerns about preventing eye infections or maintaining eye health, don't hesitate to reach out to our team. Together, we can work towards protecting your vision and preserving the health of your eyes for years to come.
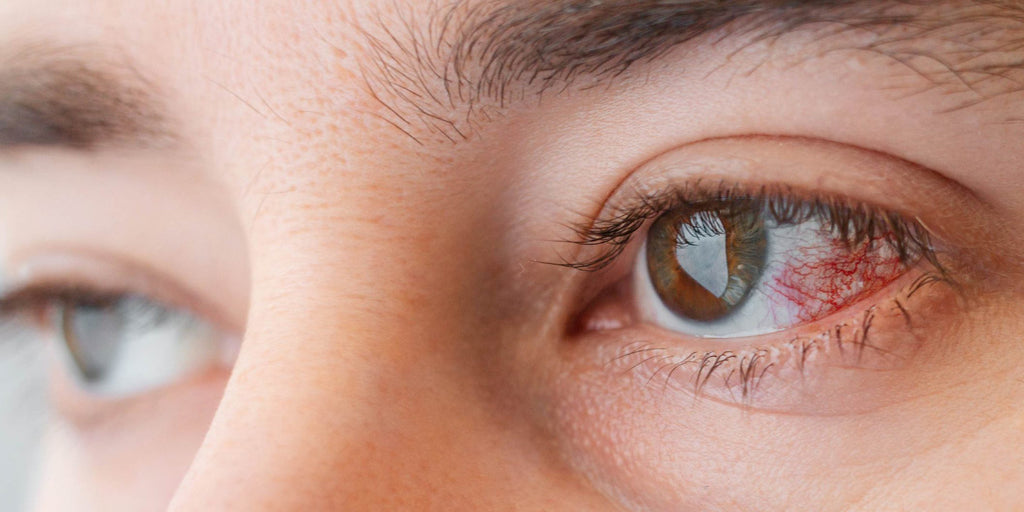

Conclusion: Empowering Your Eye Health Journey
As we conclude our exploration of eye infections—covering conjunctivitis, keratitis, uveitis, endophthalmitis, and blepharitis—we hope you've gained valuable insights into these common conditions, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options. At Look Optometry, our commitment to your eye health extends beyond providing comprehensive care; it's about empowering you to take control of your eye health journey.
We understand that navigating eye infections can be challenging, but armed with knowledge and proactive measures, you can effectively manage these conditions and safeguard your vision. Whether it's practicing good hand hygiene, maintaining proper contact lens care, or seeking prompt medical attention for symptoms of infection, every step you take plays a vital role in protecting your eyes.
Our team at Look Optometry is here to support you every step of the way. Whether you're seeking preventive care, treatment for an existing condition, or simply guidance on maintaining optimal eye health, we're dedicated to providing compassionate, personalized care tailored to your needs.
As we look ahead, our commitment to your eye health remains unwavering. We encourage you to stay informed, stay proactive, and prioritize your vision—because when it comes to your eyes, every decision matters.
Thank you for entrusting us with your eye care needs. Together, let's continue on this journey towards clearer, healthier vision. Welcome to the Look Optometry family, where your vision and well-being are our top priorities.
If you have any questions, concerns, or would like to schedule an appointment, please don't hesitate to contact us. We're here for you, and we look forward to serving you with excellence in eye care for years to come.
Learn more about Look Optometry Surrey